Maths
Mathematics, a universal language that enables understanding of the world, is an integral part of our curriculum at Dunbury Academy. Beyond the study of numbers, shapes and patterns, it also provides important tools for work in fields such as engineering, physics, finance, medicine and business. It nurtures the development of a logical and methodical mindset, as well helping to develop focus and the ability to solve all manner of problems.
Our Approach
At Dunbury we deliver maths through a teaching for mastery approach based around The Five Big Ideas: fluency, mathematical thinking, variation, representation and structure, and coherence. This is an evidence-based approach to teaching mathematics that helps pupils develop a deep, long-term and adaptable understanding of the subject. We want children to leave Dunbury as mathematical thinkers; able to problem solve, spot patterns, make connections and ask mathematical questions about the world around them.
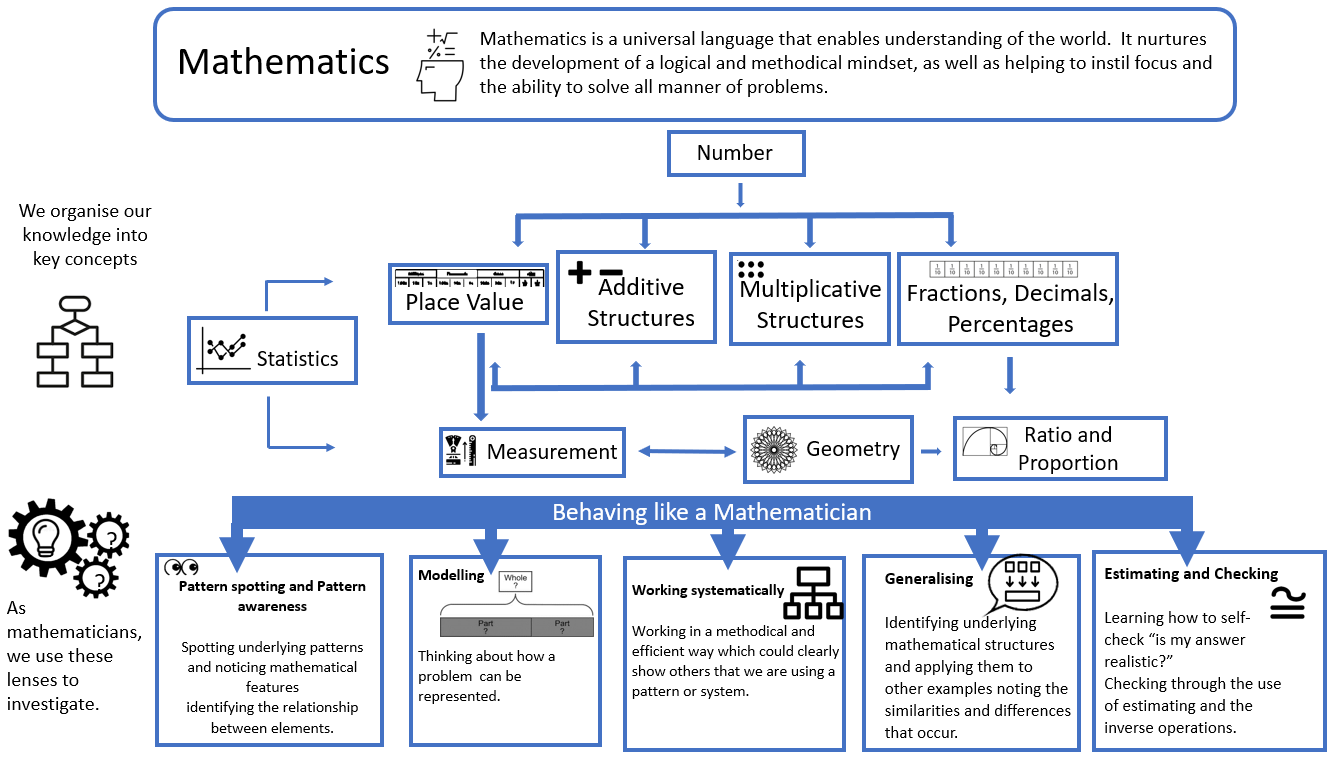
The Structure of Maths
Concepts
There are six key concepts in mathematics:
- number (which is divided into: place value, addition and subtraction, multiplication and division, fractions, decimals and percentages
- ratio and proportion,
- algebra,
- measurement,
- geometry and statistics.
Our curriculum is driven by curiosity, language and resilience. Pupils at Dunbury are encouraged to be curious about mathematics and use the disciplinary concepts (working as a mathematician) to support their approach, asking themselves:
- What do I notice?
- How can I represent this? (using physical resources and pictures)
- What is the equation? (what is the summary / process of the problem)
- What generalisations can I use? (what do I know already that I can draw on)
How can you support your child at home?
- Click on one of the following links to see how you can support your child at home.
- Information for parents Multiplication tables check
- Maths Strategies Autumn 16.10.24.pdf
- Maths strategies booklet.pdf
Fluency
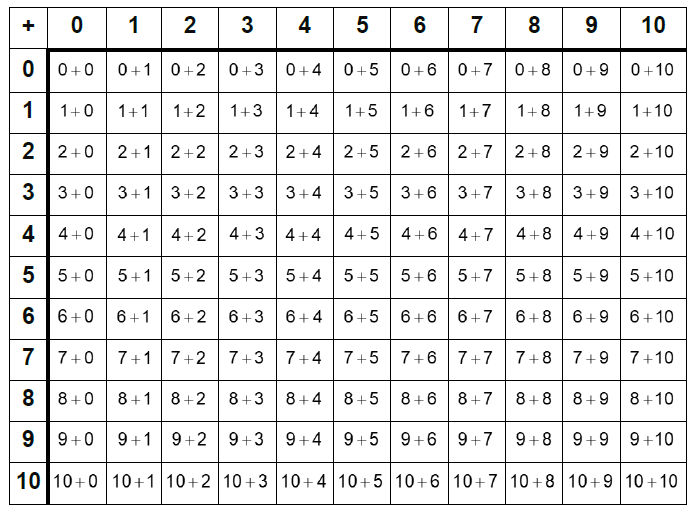
What is fluency?
Fluency is the quick and efficient recall of facts and procedures and the flexibility to move between different contexts and representations of mathematics. By the end of Year 2, children are expected to know by heart the following addition and corresponding subtraction facts:
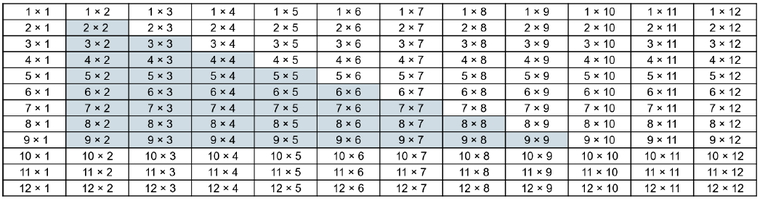
By the end of Year 4, children are expected to know all times table facts up to 12 x 12. The 36 most important facts are highlighted in the table. Fluency in these facts should be prioritised because, when coupled with an understanding of commutativity and fluency in the formal written method for multiplication, they enable pupils to multiply any pair of numbers:
Year 4 children will be expected to take a multiplication check in June. This is completed electronically. Children can practise for this using Times Table Rock Stars: https://play.ttrockstars.com/auth/school/student
This website also provides practise very similar to the multiplication check: https://www.timestables.co.uk/multiplication-tables-check/

